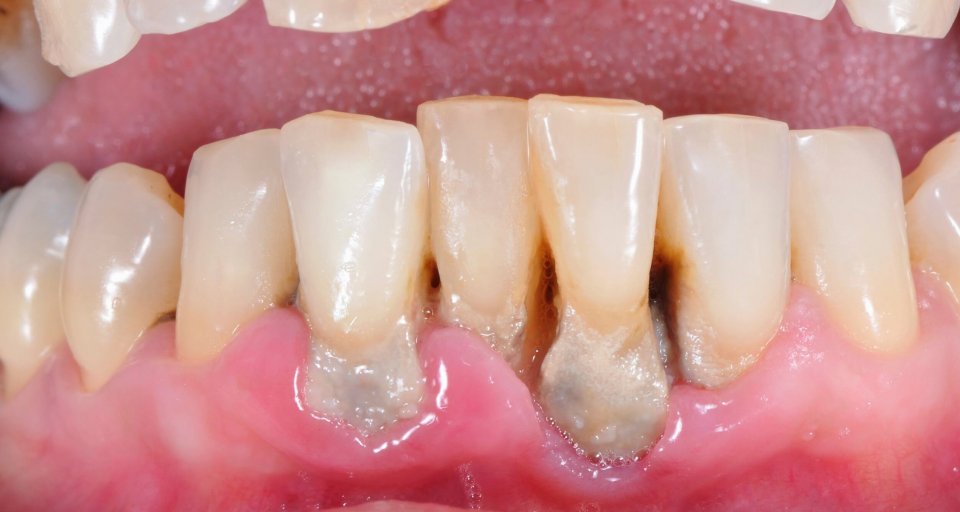
Yes, just like your hairline, your gums can recede. But unlike a hairline, gum recession isn’t always caused by genetics, although it can be. We’ll talk about common symptoms and causes of gum recession, also known as gingival recession, plus some treatment options to help your gums recover.
Symptoms of gum recession
If you’re experiencing one or more of these classic symptoms of gum recession, don’t ignore it. Be sure to consult your dentist or periodontist right away.
- Bad breath and swollen, tender or bleeding gums – Gingivitis is an early form of gum disease caused by bacterial infection. Left untreated it can advance to periodontal disease, causing the gums to recede and the teeth to possibly loosen.
- Tooth sensitivity – Beneath your tooth’s enamel and cementum is dentin, which contains small hollow tubes and canals. When the dentin is exposed, heat and cold make its way through the tubes and canals and stimulate the nerves inside your tooth causing sensitivity.
- Longer-looking teeth – When your gum pulls back away from your tooth, more tooth is exposed giving the appearance that it is longer.
- Exposed roots – If you have severe gum recession, you will be able to see your tooth’s root.
Causes of gum recession
A number of factors can contribute to gum recession including genetics, lifestyle choices and oral hygiene. Below are some of the most common causes of gum recession.
- Genetics — You may be predisposed to gum recession if either of your parents had it
- Gum disease – Bacterial infections of your gum can destroy the soft tissue and bone
- Poor oral health – Inadequate brushing and flossing can allow plaque and tartar to build up, leading to periodontitis and gum recession
- Aggressive brushing — Intense, wrong or too frequent brushing can wear away the enamel
- Crooked teeth – Misalignment can cause excessive force on the gums and bone, leading to gum recession
- Grinding or clenching your teeth – Excessive force on the teeth can cause gums to recede
- Trauma – Injury can cause the gum tissue to pull away from your teeth
- Tobacco use – Sticky plaque buildup from tobacco can lead to gum disease and recession
- Lip or tongue piercings – Constant rubbing can irritate and wear away the gums
- Hormones – Hormonal imbalances and fluctuations typical during puberty, pregnancy, and menopause can contribute to gum sensitivity, inflammation, and recession
Treating gum recession
So, can receding gums grow back? Gums can recover, but not without treatment. The type of treatment you need depends on the severity of your gum recession. If you only have mild gum recession, your dentist will likely perform a deep cleaning known as tooth scaling and root planning to help reverse it. During tooth scaling, your dentist will remove any plaque and tartar deposits from your teeth and below your gum line. During root planning, your dentist will smooth any rough surfaces on your roots. This helps keep bacteria, plaque, and tartar from sticking and gives your gums time to heal.
In addition to treating the problem, your dentist will also help you understand what caused your gum recession so that you can prevent new damage. For example, if your gum recession was caused by improper oral hygiene or aggressive brushing, your dentist will give you recommendations on the type of toothbrush to use and how to properly brush and floss. If your gum recession was caused by clenching or grinding your teeth at night, your dentist will likely recommend that you get a night guard.
If you have more severe gum recession, your dentist may recommend surgery and refer you to a periodontist for the procedure. There are three types of treatment options for gum recession — pocket depth reduction, regeneration and gum grafting. The type that’s right for you depends on the severity and cause of your gum recession.
- Pocket depth reduction – Used to clean out the pockets of bacteria, plaque and tartar that has accumulated between your gums and teeth
- Regeneration – Used to regenerate lost bone and tissue
- Gum grafting – Used to transfer a healthy flap of tissue (such as from the roof of your mouth) to the affected gum tissue and exposed root
Stop gum recession
If you’re experiencing any of the symptoms of gum recession, make an appointment with your dentist or periodontist as soon as you can for a comprehensive evaluation and recommended treatment. If you don’t have dental insurance to help offset the cost of your visit, look into getting a dental savings plan. It works like a club membership and allows you to enjoy discounts between 10% and 60% off most dental procedures, including orthodontics, and restorative and cosmetic dental work.
Plus, dental savings plans don’t have a waiting period, which is especially important when you have dental care needs that need to be addressed sooner rather than later, such as gum recession.
Practice good oral hygiene
Your oral health plays a big part in your overall health. And with most things, it’s easier to prevent something (gum recession) that it is to treat it. Now that you know some of the common causes of gum recession, be kind to your teeth and gums. It can go a long way.